Green and Sustainable Chemistry
Innovative Technology for Waste Reduction and Synthesis of Useful Chemicals
Overview
The green chemical industry focuses on the development and manufacturing of products and processes that minimize or eliminate chemical hazards and pollution. Heavily driven by innovation, firms in the green chemistry sector are actively working on improving resource efficiency and waste management by researching alternative solutions and converting chemicals of concern into useful additives, sustainable fuels, or feedstocks.
Challenges of Green Chemistry
Minimizing the production of harmful chemicals and implementing greener technologies has its own hurdles. It requires high upfront investment in new technologies that don’t exist yet or cannot maintain quality at production scale. Even if successfully developed, new technologies can be rejected by the public if they don’t seem as efficient as traditional methods at a glance, making innovation a tedious and time-consuming process.
High Initial and Regular Costs
Developing and implementing green technologies often requires significant upfront investment in new equipment, materials, and training. Opting for the use of green alternative solvents and reagents can increase regular costs as well, as they’re less readily available than their traditional counterparts.
Low Market Acceptance
There can be resistance from both businesses and consumers to adopting new, greener products and processes, especially if they are perceived to have higher costs or lower performance.
Innovation at Production Scale
Moving from laboratory-scale green chemistry innovations to industrial-level production presents significant challenges in terms of process stability, cost-effectiveness, and maintaining efficiency and quality at larger scales.
Lack of Green Solutions
For some processes, viable green solutions either don’t exist yet or are still in development. Discovering new, sustainable synthetic pathways and designing inherently safer chemicals requires substantial research and development.
Complex Regulatory Environment
Navigating complicated and sometimes slow-moving environmental regulations can hinder the adoption of new green chemical technologies. Getting the appropriate certifications can be time-consuming and costly, moreover, firms that don’t comply can face serious consequences like penalties and reputational damage.
Sustainable Solutions for Your Lab
To combat challenges related to synthetic difficulties, we encourage scientists to implement continuous flow technologies. ThalesNano’s solutions provide a safe and sustainable alternative for the green chemistry sector.
Cost-effective Green R&D
Our reactors have a wide parameter scope, which can activate less reactive materials with ease (e.g. alkylations with alcohols). High temperatures (up to 450°C) and high pressures (up to 100/200 bar) allow for the use of a wide variety of environmentally friendly solvents as well.
Easy-to-use, Efficient Technology
ThalesNano instruments can significantly reduce reaction times (from months to days) while retaining their user friendliness, making significant contributions to lab processes from the beginning.
Opening Pathways to Scale-up
Chemists can precisely control and monitor reaction parameters in real-time to quickly determine the most optimal reaction conditions while avoiding the formation of harmful intermediates. Our reactors can scale up reactions from mg to kg-scale and provide reliable results for production scale.
Difficult Reactions Made Accessible
The benefits of flow chemistry allow for difficult homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions, like aromatic ring saturations and CO2 conversion into useful additives.
Regulatory Compliance
Continuous flow chemistry systems are designed to be safe and easy-to-operate, enabling chemists to increase reaction reproducibility while bypassing many regulatory hurdles they would otherwise have to consider.
Choose Your Desired Output
H-Cube® Advance
- Temperature range: 0 - 150 °C
- Pressure range: Atm. to 100 bar
- Solvent and reagent flow rate range: 0.001-10 mL/min
- Internal hydrogen gas flow rate range: 1-70 NmL/min
- Built-in MFC for precise gas control
- Hydrogen purity: ≥ 99.9% (3.0)
- External gas inlet to connect additional gases
- External water reservoir
Phoenix Flow Reactor
- Temperature range: Amb. - 450 °C
- Pressure range: Atm. to 200 bar
- Solvent and reagent flow rate range: 0.001-30 mL/min
Connect it to the H-Genie®
- Hydrogen purity: ≥ 99.99% (4.0)
- Hydrogen gas flow rate range: 100 - 1000 NmL/min
- Water reservoir: 3000 mL
Instrument Fleets
- Modular, highly customizable, and scalable platform for a wide range of reaction types including multi-step synthesis
- Can consist of multiple flow reactors, hydrogen generators, gas and liquid inputs
- Seamless reaction parameter control and monitoring
- Generates hydrogen gas on-demand, eliminating the need for hydrogen cylinders
- Simultaneous parallel experiments can be controlled from a single user interface
- Third-party analytical devices or add-ons can be connected to the system
Green Chemistry Applications
- CO2 capture: Conversion of carbon dioxide into fuels and organic solvents to reduce greenhouse effect and enhance climate neutrality.
- Valorization: Conversion of waste materials or biomass into valuable chemicals and fuels.
- Biofuel synthesis: Conversion of natural compounds like alcohols and sugars into hydrocarbons, resulting in sustainable biofuels.
- Petrochemical additives: Synthesis of useful additives to improve fuel efficiency and increase fuel octane number to reduce emissions and harmful combustion side products.
- Rubber waste reduction: Hydrogenation and thermal treatment of rubber waste to valorize problematic materials.
Scientific Studies
Carbon-Dioxide Conversion into Sustainable Fuels
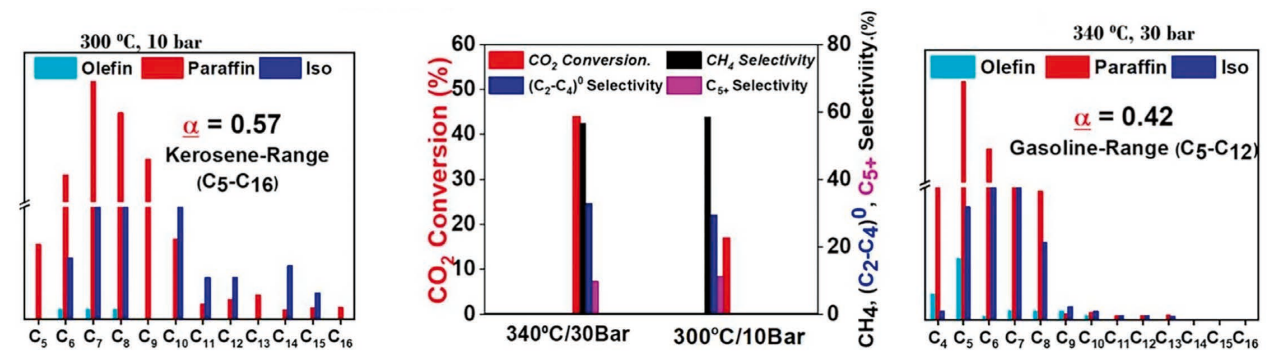
This application note highlights how ThalesNano’s H-Genie® hydrogen generator enables safe and sustainable CO2 conversion into fuels using iron-based MOF catalysts in continuous flow. By generating high-purity hydrogen directly from water, the system eliminates the need for gas cylinders and allows precise, long-term testing under industrially relevant conditions. Researchers demonstrated the conversion of CO2 into paraffin hydrocarbons (C5–C16 range) with up to 44% efficiency at optimized temperatures and pressures, achieving excellent catalytic stability over 100+ hours.
Coupled with ThalesNano’s reactor technologies and automation software, this platform showcases a scalable and safe route to producing sustainable fuels while reducing greenhouse gas emissions—offering chemists and engineers a practical solution for carbon capture and utilization.
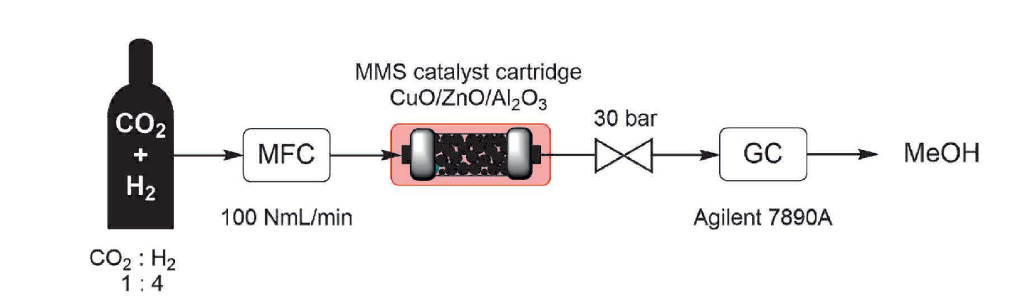
Value-Added Chemical Production from a Low-Cost Renewable CO2 Source
Our application note demonstrates how the Phoenix Flow Reactor can be applied for high-pressure CO₂ hydrogenation to produce methanol and other value-added chemicals. Using a CuO/ZnO/Al₂O₃ catalyst prepared in-house, our application chemists operated a Phoenix Flow Reactor paired with a Gas Module at up to 300 °C and 30 bar, with precise gas dosing and online GC analysis. The setup achieved nearly 70% selectivity toward methanol, showing strong catalytic performance under continuous gas-phase conditions.
Designed to handle up to 450 °C and 200 bar, the Phoenix Flow Reactor provides a safe, flexible, and scalable platform for CO₂ utilization studies, including carbon capture. Looking ahead, this approach can be extended with advanced catalysts (e.g., H-ZSM-5) to target longer-chain hydrocarbons, paving the way for sustainable fuel production from renewable carbon sources.
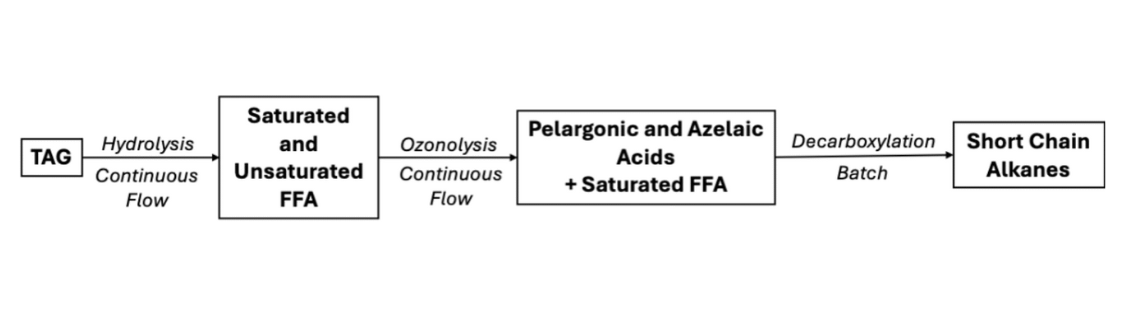
Chemo-enzymatic Cascade Methodology for Sustainable Canola Oil Conversion
This RSC Sustainability study introduces a chemo-enzymatic cascade for the sustainable conversion of canola oil into hydrocarbon fuels, integrating enzymatic biocatalysis with continuous-flow technology. The process begins with the enzymatic hydrolysis of canola oil using Candida rugosa lipase, achieving >99% conversion of triglycerides into free fatty acids under both batch and continuous-flow conditions.
The resulting fatty acids were then modified either by continuous-flow hydrogenation using a ThalesNano H-Cube® Mini Plus equipped with Pd/C CatCarts® to yield saturated fatty acids, or by ozonolysis to produce mono- and dicarboxylic acids. In the final stage, enzymatic photodecarboxylation was carried out with Chlorella variabilis fatty acid photodecarboxylase (CvFAP) under violet light irradiation in a ThalesNano PhotoCube, enabling efficient conversion of fatty acids into long-, medium-, and short-chain alkanes. The cascade delivered high conversion and selectivity (>90–99%) while reducing energy input, operational time, and waste.
By combining enzymatic and chemical catalysis in continuous flow, the work provides a robust and scalable methodology for producing renewable drop-in hydrocarbon fuels, highlighting the role of flow reactors and photobiocatalysis in advancing green energy technologies.
Scrap Waste Powder Characterization and Conversion into Biomass-derived Chemicals
A publication from Green Chemistry made by Luque et al. investigates the catalytic activity of scrap ceramic-cores of automotive catalytic converters (SCATs) by continuous flow hydrogenation of different biomass-derived compounds. Prior to and after catalytic use, waste SCAT powders were thoroughly characterized using ICP-MS, TGA, MP-AES, XRD, N₂ physisorption, TPR, HRTEM, and EDS.
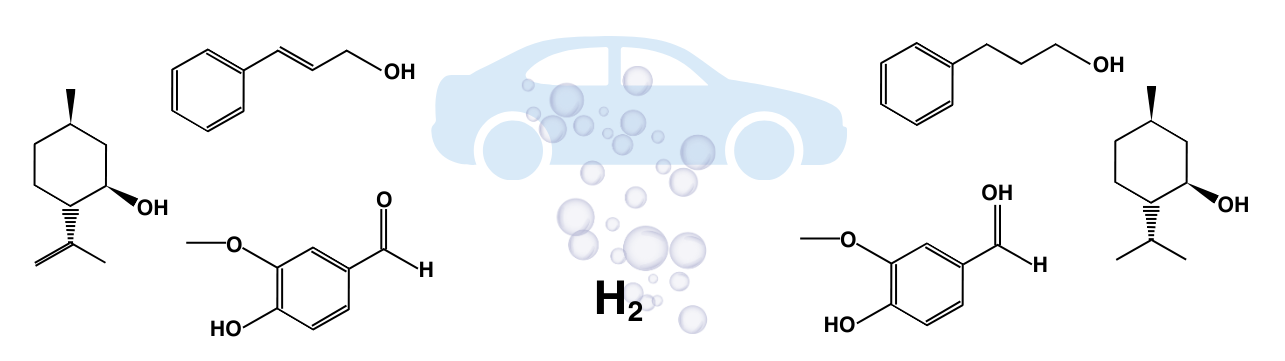
Hydrogenations included the conversion of isopulegol to menthol, cinnamyl alcohol to hydrocinnamyl alcohol, isoeugenol to dihydroeugenol, vanillin to vanillyl alcohol, and benzaldehyde to benzyl alcohol, utilizing the H-Cube® Mini Plus continuous flow reactor’s precise control over reaction parameters like temperature, pressure, flow rate, and substrate concentration.
Remarkably, continuous flow technology allowed these waste-derived catalysts to exhibit high performance and stability despite their low metal content, a result attributed to the synergistic presence of multiple noble metals and the unique composite structure of the material.
More Knowledge
FAQ
Our continuous flow reactors are designed to be able to perform heterogeneously catalysed hydrogenations using in-situ generated hydrogen, which eliminates the need for hydrogen storage and complies with green and sustainable chemistry.
Our systems can be used for research in carbon capture and the reduction of CO2 emissions, as well as waste valorization and the synthesis of sustainable fuels and additives.
Our catalyst cartridges (CatCart®s) can generally be regenerated after a reaction (unless working with starting materials of potent poisoning effect such as thiols/thiophenes). In an ideal case, one cartridge can convert up to ~10 grams of material.
Do you have more questions?
Reach out to us at any time and experience fast and efficient support tailored to your specific needs.