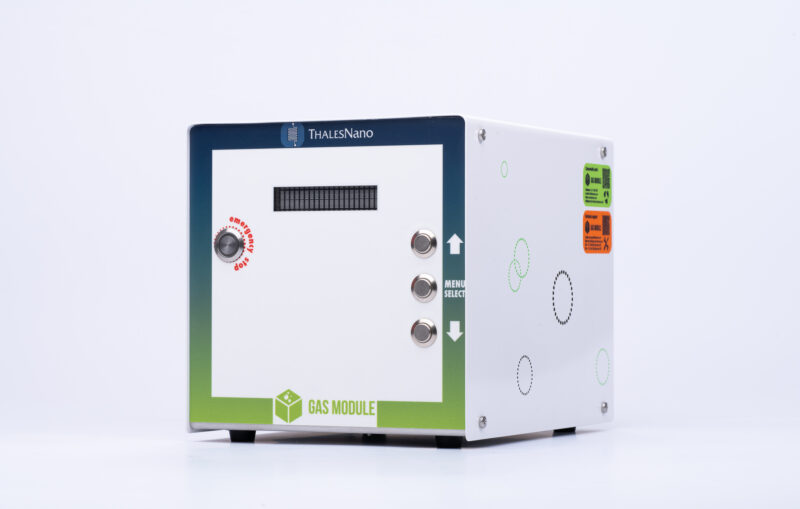
Gas Module
Reactions with gases made easy
Accurate Gas Dosing
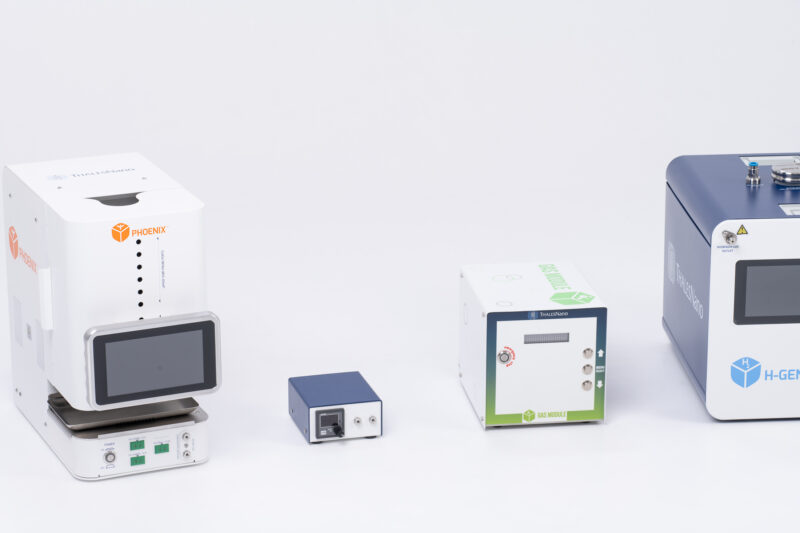
This module enables precise dosing of various gases, offering a seamless integration of gas handling capabilities into your workflow. It supports a wide range of gases, including hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and more, allowing you to tailor the gas environment to meet your specific experimental requirements. The Gas Module seamlessly integrates with other ThalesNano instruments and modules (including the H-Cube Pro and the Phoenix Flow systems), allowing for comprehensive control of your laboratory processes.
How does the Gas Module work?
The module can work easily with the H-Cube Pro and with the Phoenix Flow Reactor to allow different gases to be used up to 100 bar pressure. Reactions, such as carbonylations or oxidations, can be performed at high pressures, widening the reactor’s chemistry ability significantly.
- A gas source, typically a gas cylinder, connected to the module lets out a gas flow that should be in a pressure range between 25 and 140 bar.
- Users can select the applicable gas from the list of the module or set the properties of a new gas.
- The built-in mass flow controller ensures the accurate dosing of the gas, even at high pressure.
Features
Versatile: 14 gases in one device: compressed air, O2, CO, ethylene, SynGas for hydroformylations, CH4, C2H6, He, H2, N2, N2O, NO, Ar, CO2 (after preheating); other gases with well-known thermodynamic properties and compatibility can be introduced
Powerful: Capability for performing heterogeneous reactions at up to 100 bar pressure
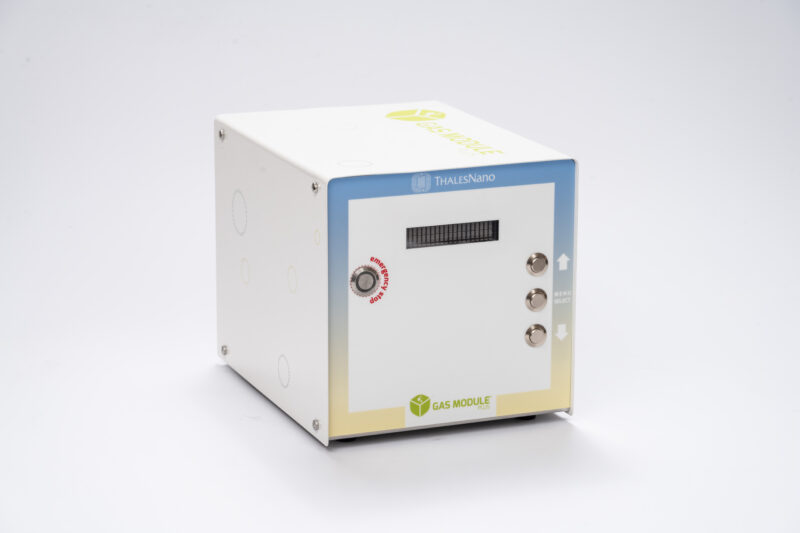

Gas Module Plus
The Gas Module Plus is purpose-built for accommodating larger quantities of gases. It seamlessly integrates with ThalesNano reactor systems, such as the H-Cube Pro and the Phoenix Flow systems. This module guarantees precise and controlled gas dosing at flow rates of up to 1 NL/min, extending the gas flow range.
Use it with the H-Cube Pro
When the module is connected to the H-Cube Pro, it allows the introduction gases, such as carbon monoxide, oxygen or syngas.
Use it with the Phoenix Flow systems
Connect multiple modules to the Phoenix Flow reactor to set up a system for catalytic reactions with different gases.
Specifications
| Technical data | |
|---|---|
| Inlet Pressure: | Minimum: 25 bar, Maximum 140 bar |
| Outlet Pressure: | Maximum 100 bar |
| Flow Rates (N2): | 0 – 100 NmL/min (Gas Module), 100-1000 NmL/min (Gas Module Plus) |
| MFC Calibrating Gas: | Nitrogen |
| Dimensions: | Height: 21 cm (8.27”) Width: 20 cm (7.87”) Depth: 30 cm (11.8”) |
| Weight: | 8 kg (17.6 lbs) |
| Power requirements: | 115-230VAC 47-63Hz, 50VA |
| Fuses: | 2×1A-T/230VAC 2×1.6A-T/115VAC |
| Gas inlet connection: | male 1/8” OD stainless steel, 5/64″ ID, 1/64″ wall connection |
| Gas outlet connection: | 1/16” stainless steel line with Swagelok fitting and ferrule |
FAQ
The vapor pressure of each gas is given in the below table.
Gas name | Gas type | Vapor pressure |
Air | Air | NA |
Argon | Ar | NA |
Ethylene | C2H4 | NA |
Ethane | C2H6 | 543 psi (37 bar) |
Methane | CH4 | Non condensable |
Carbon Monoxide | CO | NA |
Carbon Dioxide | CO2 | 838 psi (58 bar) at 20 °C (preheater is needed to avoid condensation) |
Hydrogen | H2 | NA |
Helium | He | NA |
Nitrogen | N2 | NA |
Dinitrogen monoxide | N2O | 736 psi (50 bar) at 20 °C |
Nitrogen monoxide | NO | 508 psi (35 bar) at 20 °C |
Oxygen | O2 | NA |
Synthesis gas | Syn | NA |
Gas name | Gas type | Max. flow rate (NmL/min) | Max. flow rate (mmol/min) | Max. flow rate (mg/min) |
Air | Air | 100 | 4.46 | 128.8 |
Argon | Ar | 140 | 6.23 | 248.4 |
Ethylene | C2H4 | 62 | 2.77 | 77.4 |
Ethane | C2H6 | 50 | 2.19 | 65.7 |
Methane | CH4 | 76 | 3.39 | 54.2 |
Carbon monoxide | CO | 100 | 4.44 | 124.4 |
Hydrogen | H2 | 101 | 4.5 | 9.1 |
Helium | He | 139 | 6.19 | 25 |
Nitrogen | N2 | 100 | 4.46 | 125 |
Dinitrogen monoxide | N2O | 76 | 3.36 | 147 |
Nitrogen monoxide | NO | 100 | 4.46 | 133.9 |
Oxygen | O2 | 99 | 4.41 | 141.3 |
Synthesis Gas | Syn | 100 | 4.46 | 62.2 |
Do you have more questions?
Reach out to us at any time and experience fast and efficient support tailored to your specific needs.




