Deuteration
Explore a new way to perform reactions with deuterium gas
Deuterium-labeled compounds in chemistry
Deuterium-labeled compounds have an important role as valuable research tools in the field of chemistry. Applications of deuteration reactions include:
Proving reaction mechanisms: Deuterium-labeled compounds provide a way to investigate reaction pathways and mechanisms. By selectively replacing hydrogen atoms with deuterium atoms, researchers can follow reaction steps, unraveling important details of a chemical transformation.
Investigation of the pharmacokinetic properties: Understanding the behavior of chemical compounds in biological systems is crucial for drug discovery. Deuterium-labeled molecules enable researchers to trace the metabolism, absorption, distribution, and elimination of compounds accurately.
Internal standards in mass spectrometry: Mass spectrometry is a fundamental analytical technique used to identify and quantify compounds. By using deuterium-labeled compounds as internal standards, researchers can increase the accuracy and reliability of their measurements, providing precise identification and quantification of the target compounds.
Chemical structure determination in NMR spectroscopy: Deuterium-labeled molecules are extensively used in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy, providing valuable information about molecular structures.
How to streamline deuteration with the help of the H-Cube systems
The conventional methods for the synthesis of deuterated compounds utilize D2 gas as the deuterium source, however, they have drawbacks. Other approaches have been employed to overcome the difficulties, such as catalytic H-D exchange reactions between H2 and D2O. These methods are usually time consuming, they do not produce high purity D2 and require high pressure, special catalyst or excess amount of a strong base or acid.
The H-Cube Mini Plus and the H-Cube Pro continuous flow systems make deuteration effortless. These instruments are capable of generating deuterium gas from the electrolysis of D2O with 99,98% purity, which can be used safely and easily in continuous flow reactions.
Deuteration with H-Cube reactors
In recent years, a significant amount of knowledge and experience has been gathered and published in the field of deuteration reaction in continuous flow. A couple of illustrative examples:
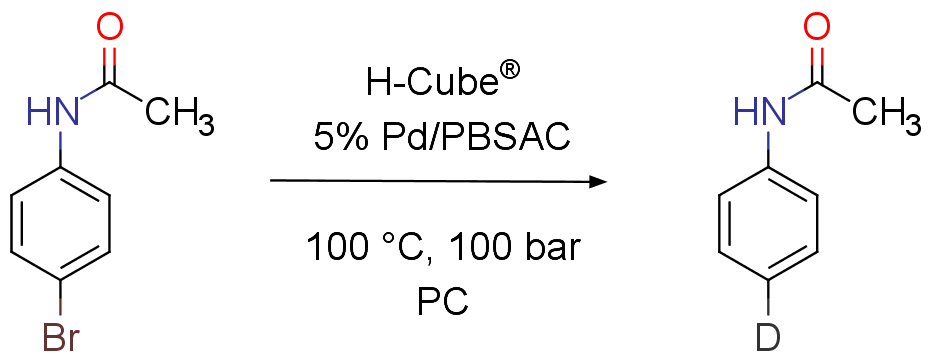
Continuous flow catalytic deuterodehalogenation
Orsy, G.; Fulop, F.; Mandity, I. M.; Green Chemistry, 2019, 21, 956-961
Switching from water to deuterium oxide (H-Cube Mini Plus)
- Replace the catalyst cartridge with an inert CatCart. Remove the deionized water from the water reservoir.
- Fill the water reservoir and with 10 mL of heavy water.
- Run a blank reaction with H2 ON setting to remove water residues from the water line.
- Open the water reservoir and remove the normal-heavy water mixture.
- If it is important to remove traces of normal deionized water, repeat the points 2-4.
- Fill the water reservoir with heavy water.
Switching from water to deuterium oxide (H-Cube Pro)
- Replace the catalyst cartridge with an inert CatCart. Remove the deionized water from the water reservoir.
- Push the water tank purge on the info screen and wait 30 seconds to remove the remaining water.
- Close the water reservoir and fill it with 10 mL of heavy water.
- Use the water tank purge on the info screen and wait 1 minute to wash the water line properly with heavy water.
- Open the bottom of the water reservoir and remove the normal-heavy water mixture.
- Push the water tank purge on the info screen and wait 30 seconds to remove the remaining normal-heavy water mixture.
- Close the water reservoir and fill it with heavy water.
- If it is important to remove the traces of the normal water, repeat the points 4-7.
- Start using the system with heavy water.
- Place the new cartridge into the H-Cube Pro and run heavy water through for a simulated run prior to the planned reaction.